How to set up the solution?
How much does it cost?
Go to: Future Finance
Where does the data come from?
Your accounting software, for example Merit Aktiva.
How to update app and change parameters?
Option 1 – You work in Power BI workspace
Update
When a new version of the app becomes available, you will see a notification in your workspace:
Get it now > Install
You have the option to update your current workspace and app, or alternatively, create a new workspace to preserve the older version.
Note! If you decide to update the existing workspace and the app, the workspace name will automatically be changed to the app’s name with current date. However, you can go to the workspace settings and manually rename it.
Change parameters
If you wish to modify your parameters (such as API ID, start period, etc.), navigate to your workspace. Locate the three dots next to your dataset, click on them, and select ‘Settings’. In the ‘Parameters’ section, you can make the desired changes.
Option 2 – You work on the Future Finance webpage
App will be updated for you.
How does it work?
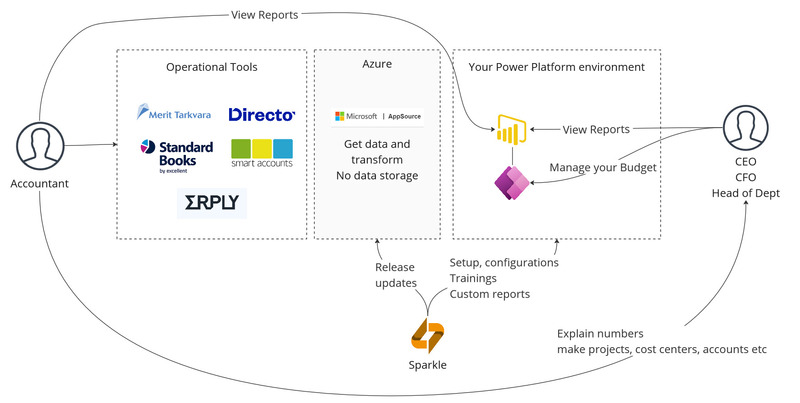
Who does what and where?
Main financial measures
Assets
An asset represents an economic resource owned or controlled by a company. An economic resource is something that may be scarce and has the ability to produce economic benefit by generating cash inflows or decreasing cash outflows.
Cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold (COGS) refers to the direct costs of producing the goods sold by a company. This amount includes the cost of the materials and labor directly used to create the good. It excludes indirect expenses, such as distribution costs and sales force costs.
Current Cashflow
Transactions related with cash movement (cash, bank)
EBIT
Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) is a company’s net income before income taxes. It is used to analyze the performance of a company’s core operations without tax expenses and the costs of the capital structure influencing profit
EBITDA
Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (used as an indicator of the overall profitability of a business)
Gross profit
The amount of money a company earns from its core business operations after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS)
Gross profit margin
Gross profit margin is a metric analysts use to assess a company’s financial health by calculating the amount of money left over from product sales after subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS). Gross profit margin is frequently expressed as a percentage of sales.
Liquidity ratio
The liquidity ratio measures the company’s ability to cover its short-term obligations with its current assets. It is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities. A higher current ratio indicates a better ability to meet short-term obligations.
Net profit/loss
A measure of a company’s profitability after deducting all expenses, including both operating and non-operating costs, from its total revenue
Revenue
Revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods and services related to the primary operations of the business
ROA
ROA stands for Return on Assets. It is a financial ratio that measures a company’s profitability by evaluating its ability to generate earnings from its assets.
ROE
ROE stands for Return on Equity. It is a financial ratio that measures a company’s profitability by evaluating the return it generates on the shareholders’ equity. ROE indicates how effectively a company utilizes its shareholders’ investments to generate profits.
Total liabilities
A liability is something that company owes
Working capital
Working capital refers to the difference between a company’s current assets and current liabilities. It represents the funds available to a company for its day-to-day operations, such as paying suppliers, covering operating expenses, and managing short-term obligations.
